Spotters A1
Slide 2
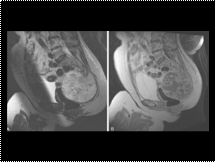
Sacrococcygeal chordoma
Slide 3
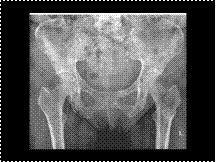
Multiple myeloma
Slide 4
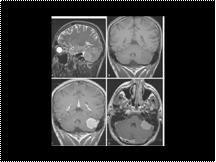
Meningioma along the posterior side of the left temporal bone. A, T2-weighted sagittal MR image. The tumor has an intermediate to slightly hyperintense signal. B, T1-weighted coronal nonenhanced MR image. The tumor is hypointense compared to the adjacent cerebellum. C, T1-weighted coronal contrast-enhanced MR image. There is intensive, homogeneous enhancement of the tumor. D, T1-weighted axial contrast-enhanced MR image. Note the enhancement of the adjacent dura (“dural tail”).
Slide 5
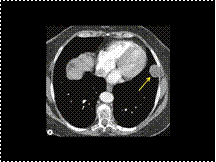
localized fibrous tumor of the pleura
Slide 6
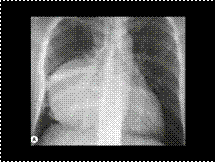
Mature teratoma
Slide 7
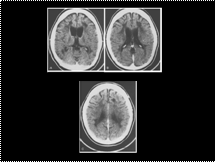
Metachromatic leukodystrophy
Slide 8
fat necrosis
Slide 9
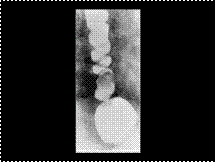
Diffuse esophageal spasm
Slide 10
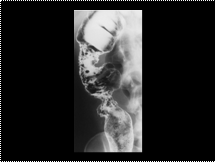
Tuberculosis
Slide 11
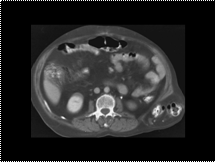
Lumbar hernia through the inferior triangle.
Slide 12
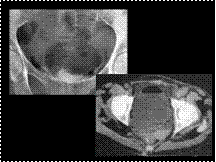
Emphysematous cystitis
Slide 13
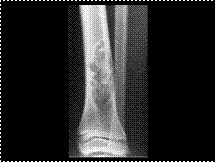
Fibrous cortical defect
Slide 14
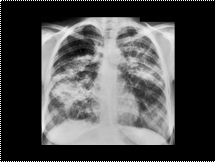
Pulmonary fibrosis caused by sarcoidosis. The mid- zone predominance radiating from the hila with relative sparing of extreme apices and bases is typical of sarcoidosis
Slide 15
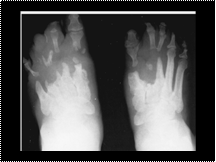
Leprosy. Marked bone destruction and pencil-like resorption, most severe at the metatarsophalangeal joint
Slide 16
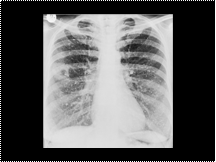
Multiple small calcifications in the lungs caused by old healed varicella pneumonia.
Slide 17
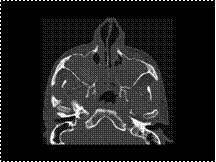
Fungal infection. Retention cysts, polyps, and fluid are usually of soft tissue density. When there is increased density within sinus cavities, as seen in the maxillary sinuses bilaterally in this patient, one must consider intrasinus hemorrhage, inspissated secretions, or fungal infection
Slide 18
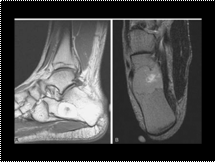
Intraosseous lipoma
Slide 19
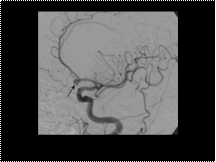
left anterior communicating aneurysm. B, The aneurysm is demonstrated on the oblique anteroposterior view of the catheter left carotid cerebral angiogram (arrow).
Slide 20
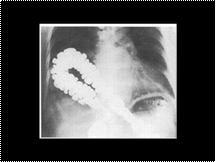
Bochldek hernia
Slide 21
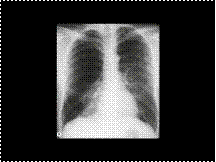
Chest radiograph shows lucency in the right hemithorax simulating pneumothorax, though the hyperlucent space is traversed by some linear strands of parenchyma
Slide 22
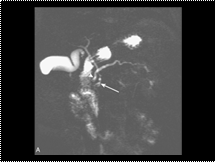
Pancreas divisum type 3
Slide 23
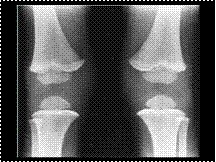
Bismuth poisoning
Slide 24
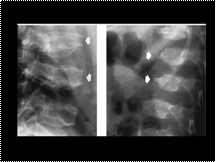
Morquio syndrome
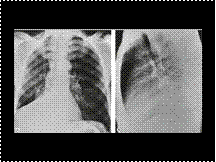
Slide 25
Combined right middle and lower lobe atelectasis.
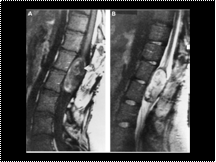
Slide 26
Epidermoid
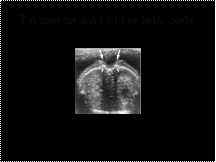
Slide 27
Spina bifida
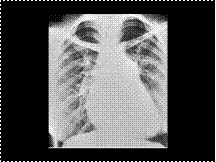
Slide 28
Pulmonary arterial hypertension
Slide 29
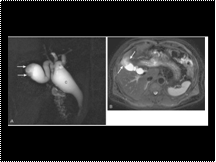
Gallbladder cancer associated with choledochal cyst
Slide 30
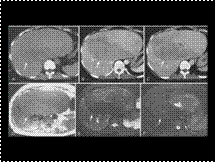
Hepatic adenoma
Slide 31
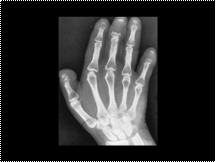
Familial acro-osteolysis. Characteristic bandlike areas of lucency crossing the waists of several phalanges.
Slide 32
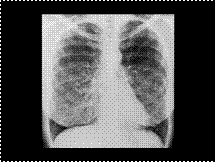
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis of lung
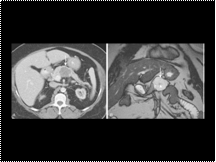
Slide 33
Axial contrast-enhanced MDCT reveals a finely lobulated lesion (arrow) with a microcystic appearance in the proximal body of the pancreas. B, Corresponding coronal T2-weighted MR image demonstrates the same findings (arrow) and also reveals a central scar (arrowhead) that is virtually pathognomonic for serous cystadenoma.
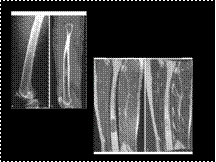
Slide 34
Enchondroma in a 56-year-old man. A, Radiograph demonstrates a lesion with a cartilaginous matrix in the distal femur. B, CT scan shows calcifications in the matrix of the lesion. C and D, Sagittal T1-weighted spin echo (C) and T2-weighted fast-spin echo (D) images demonstrate a lobulated lesion in the medullary cavity. The exact extension of the lesion is easily appreciated, but the matrix calcifications are better seen on CT.
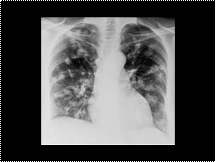
Slide 35
Multiple pulmonary nodules owing to metastases from a squamous cell carcinoma of salivary gland
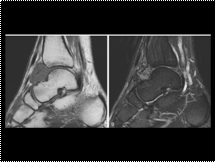
Slide 36
Pigmented villonodular synovitis
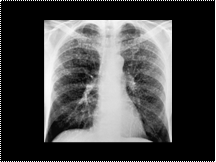
Slide 37
silicosis
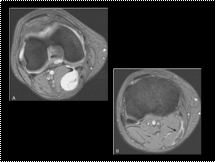
Slide 38
Popliteal cyst with rupture
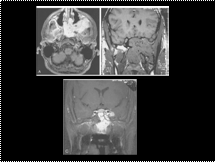
Slide 39
Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma
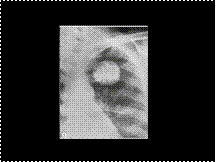
Slide 40
Popcorn calcifications in pulmonary hamartoma
Slide 41
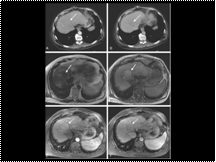
Cirrhosis and a prominent dysplastic nodule in the right hepatic lobe