Spotters A4
Slide 2
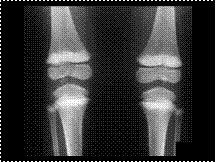
Lead poisoning
Slide 3
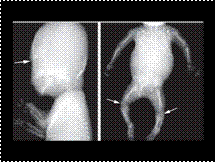
Chondrodysplasia punctata
Slide 4
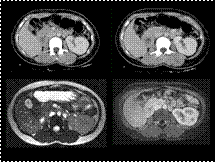
Annular pancreas with left crossed fused renal ectopia
Slide 5
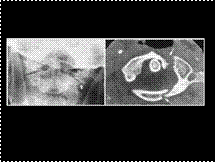
CHONDROSARCOMA
Slide 6
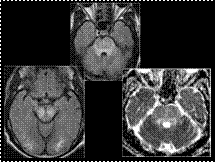
PRES
Slide 7
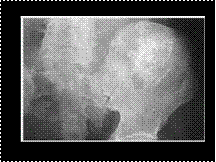
JEFFERSON’S FRACTURE
Slide 8
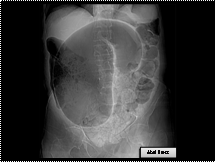
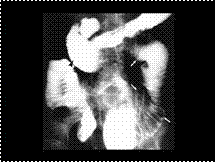
Sigmoid Volvulus
Slide 9
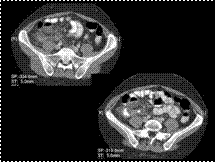
Scleroderma
Slide 10
Appendicitis with appendicolith
Slide 11
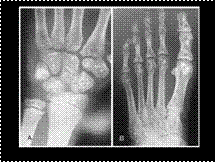
OSTEOPOIKILOSIS
Slide 12
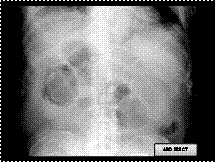
Emphysematous cholecystitis
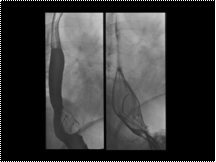
Slide 13
Esophageal leiomyoma
Differential Dx: Esophageal duplication cyst, hamartoma , lipoma, fibrovascular polyp , granular cell tumor, neurofibroma myxofibroma
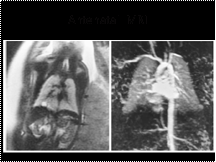
Slide 14
Type II cystic adenomatoid malformation in a 29-week-old fetus. (a) Coronal single-shot
fast spin-echo MR image shows multiple small cysts in the lower lobe of the right lung. (b) Coronal
gadolinium-enhanced MR angiogram obtained 4 days after birth clearly shows an aberrant artery from
the abdominal aorta.
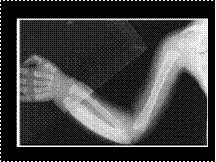
Slide 15
INFANTILE CORTICAL HYPEROSTOSIS: ULNAR INVOLVEMENT. Note involvement of the ulna, with sparing of the radius and humerus.COMMENT: The ulna is the most frequently involved long bone in infantile cortical hyperostosis
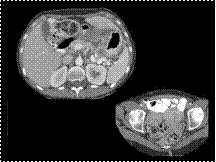
Slide 16
Krukenberg tumor, Primary Gastric adenocarcinoma
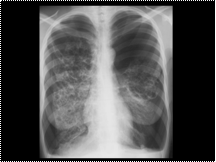
Slide 17
LCH with pneumothorax
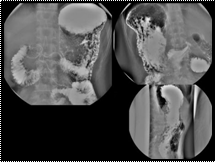
Slide 18
Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP)
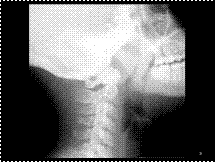
Slide 19
Enlarged Tonsils
and Adenoids
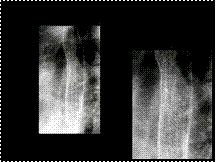
Slide 20
Feline esophagus
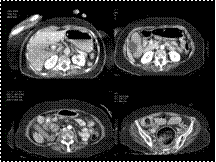
Slide 21
Acute Mesenteric Ischemia: SMA Occlusion...... Incidentally noted is a lipoma of the illeocecal valve
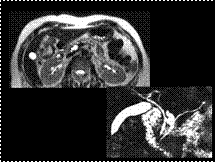
Slide 22
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm
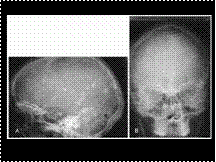
Slide 23
TUBEROUS SCLEROSIS
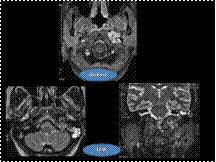
Slide 24
glomus jugulare tumor
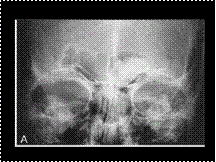
Slide 25
OSTEOMA: FRONTAL SINUS
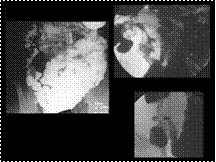
Slide 26
CROHNS DS
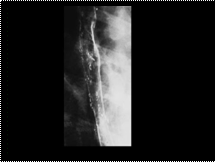
Slide 27
Esophageal intramural pseudodiverticulosis
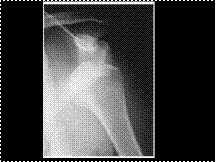
Slide 28
SUBCORACOID ANTERIOR DISLOCATION OF THE SHOULDER
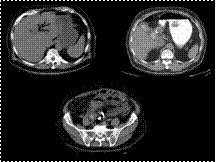
Slide 29
Gallstone ileus
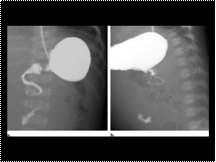
Slide 30
Malrotation with volvulus in a neonate. Radiographs obtained with barium administered via a nasogastric
tube show a corkscrew appearance of the duodenum and an abnormal position of the duodenojejunal
junction on both frontal (a) and lateral (b) views, features indicative of volvulus, which constitutes a surgical
emergency.
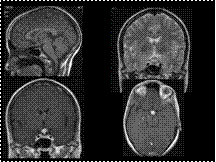
Slide 31
tuber cinerum LCH
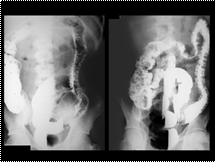
Slide 32
UC
Slide 33
Galactocele
Slide 34
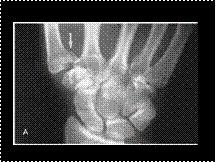
BENNETT'S FRACTURE
Slide 35
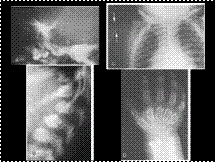
HURLER'S SYNDROME
Slide 36
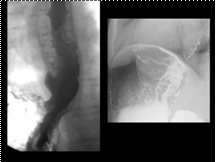
Diagnosis: GastroEsophageal varices
Differential Dx: Esophageal varices, Varicoid carcinoma of the esophagus, Inflammation of distal esophagus secondary to reflu
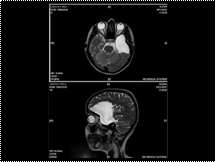
Slide 37
Arachnoid Cysts
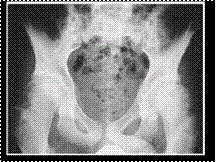
Slide 38
BILATERAL SLIPPED FEMORAL CAPITAL EPIPHYSIS
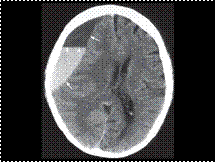
Slide 39
frontoparietal subdural haematoma (arrows) with a fluid level (arrowheads). Note the hyperdense acute component at the dependent
portion and the hypodense chronic component in the non-dependent portion.
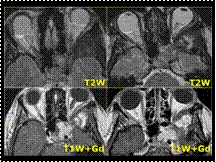
Slide 40
FD
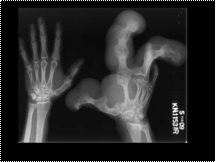
Slide 41
macrodystrophica lipomatosa
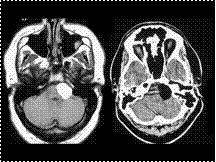
Slide 42
CPA Lipoma
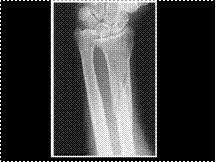
Slide 43
GALEAZZI'S FRACTURE
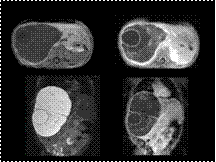
Slide 44
benign mesenchymal hamartoma of the liver.
D/D Vascular lesions of mesenchymal origin are hemangioendothelioma and cavernous hemangioma
Slide 45
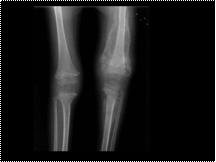
Scurvy
Slide 46
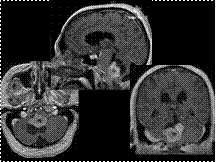
Choroid Plexus Papilloma of the 4th Ventricle DDx: Choroid plexus carcinoma, Ependymoma, Metastasis, Meningioma
Slide 47
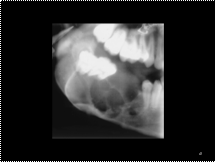
Ameloblastoma. Lateral oblique radiograph of the mandible shows an expansile, multilocular, lucent lesion with coarse internal trabeculae and displacement of teeth and adjacent structures. The differential diagnosis includes ameloblastoma and odontogenic keratocyst. (3) Ameloblastoma. Axial CT scan shows an expansile, locular, hypoattenuating lesion in the left aspect of the mandible with well-corticated buccal expansion. (4) Mural ameloblastoma. Low-power photomicrograph (hematoxylin-eosin stain) shows an ameloblastoma (T) arising from the epithelial lining (arrow) of a dentigerous cyst surrounded by a fibrous capsule (F).
Slide 48
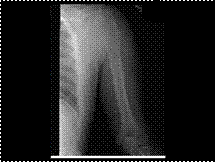
Ewings Tumor
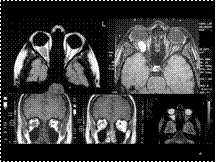
Slide 49
Cavernous Hemangioma
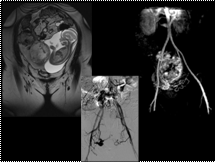
Slide 50
placental hemorrhage
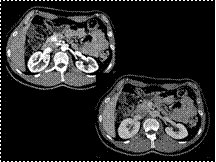
Slide 51
INSULINOMA