Spotters A8
Slide 2
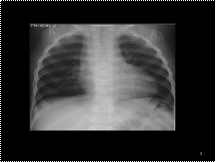
Rt.sided aortic arch in patient with cour-en-sabout heart: TETRALOGY OF FALLOT
-trachea displaced towards midline
Slide 3
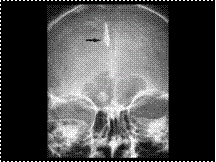
OSTEOMA: FRONTAL SINUS
Slide 4
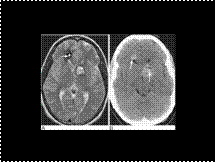
Cavernous haemangioma. (A) T2-weighted axial image showing typical mixed signal intensity lesions. High signal is due to methaemoglobin and the low signal intensity rim of haemosiderin indicates an old haemorrhage. The ‘popcorn’ appearance of the larger lesion is typical of a ‘cavernoma’. Note the blood–fluid level in the smaller lesion (arrow). (B) Unenhanced CT of the same patients shows the lesions to be predominantly high density with tiny foci of calcification (arrows).
Slide 5
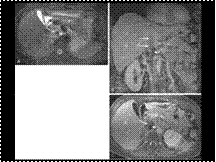
IVC LEIOMYOSARCOMA
Slide 6
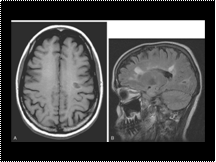
MS
Slide 7
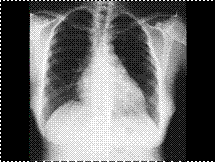
FIBROUS DYSPLASIA INVOLVING LEFT FOURTH RIB
Slide 8
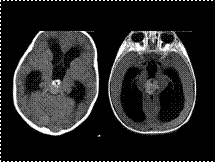
PIENOBLASTOMA
Slide 9
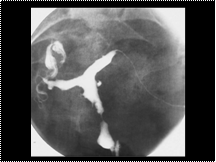
Adenomyosis. Abnormal uterine margins with contrast penetrating the myometrium.
Slide 10
AVM
Slide 11
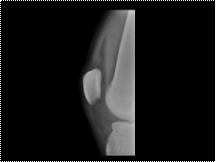
LIPOHEMARTHROSIS
Slide 12
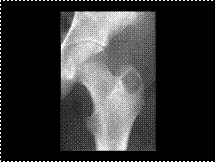
CHONDROBLASTOMA. Greater Trochanter of the Femur
Slide 13
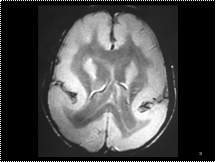
LISSENCEPHALY
Slide 14
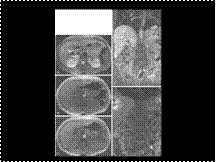
PHEOCHROMACYTOMA
Slide 15
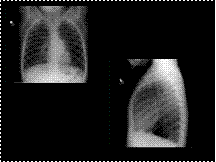
Neuroblastoma
Ganglioneuroblastoma
Ganglioneuroma
Lymphoma
Teratoma
Foregut cyst
Slide 16
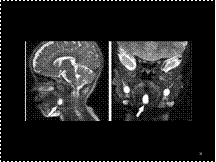
Thyroglossal duct cyst in a 3-year-old boy. Sagittal (a) and coronal (b) T2-weighted
MR images show a hyperintense midline cystic mass of the foramen cecum (arrow).

Slide 17
From left to right: straight flush; pigtail; cobra; and sidewinder. Note the side-ports in some of the catheters.
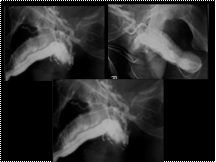
Slide 18
CAVERNOSOGRAM : VENOUS LEAK
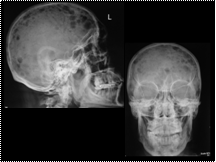
Slide 19
MM
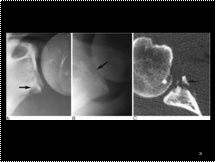
Slide 20
Bankhart injury of the inferior glenoid rim. AP (A) and axillary (B) radiographs in a patient who suffered an anterior shoulder dislocation show an irregularity in the inferior bony glenoid, consistent with a Bankhart fracture (arrow). The shoulder has been reduced. Axial CT (C) from the same patient shows the relationship of the fragment (arrow) to the glenoid.
Slide 21
HIATUS HERNIA
Slide 22
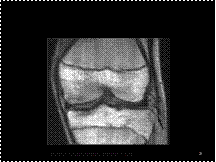
Segond fracture of the knee. Coronal proton density-weighted MRI demonstrates avulsion of the bony insertion of the iliotibial band (arrow). Avulsions of the lateral collateral ligament complex have a close association with ACL injury.
Slide 23
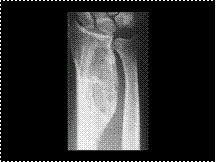
ABC
Slide 24
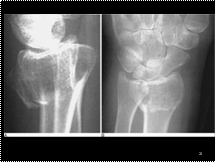
Colles fracture of the distal radius. Lateral (A) and PA (B) views demonstrate an impacted fracture of the distal radius with dorsal angulation of the distal fracture fragment. The ulnar styloid process is intact
Slide 25
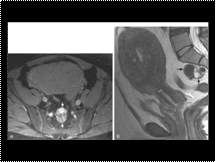
Extraperitoneal pelvic tailgut cyst in a 43-year-old woman. A and B, Axial fat-suppressed T1-weighted (A) and sagittal T2-weighted (B) images through the pelvis demonstrate a well-circumscribed multiloculated lesion (arrows) in the presacral space with variable T1-weighted and T2-weighted signal intensity in loculi due to variable amounts of proteinaceous or hemorrhagic fluid content. Note the incidentally detected uterine adenomyosis on the sagittal image, as manifested by a thickened junctional zone that contains multiple cystic foci corresponding to trapped endometrial glands
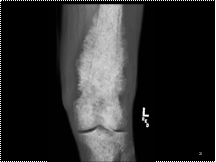
Slide 26
PROSTATE METASTASES Most skeletal metastases do NOT produce a soft tissue mass
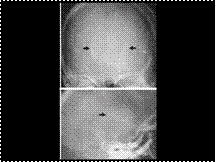
Slide 27
BG CALCIFICTION
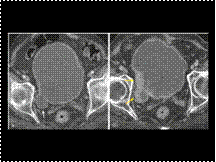
Slide 28
Development of bladder malignancy within a diverticulum. A, Initial axial CT scan shows a right lateral bladder wall diverticulum (arrow). B, Follow-up CT scan for symptomatic hematuria shows thickening and a mass lesion (arrows) within the diverticulum.
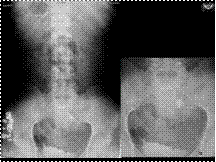
Slide 29
PANCAKE KIDNEY
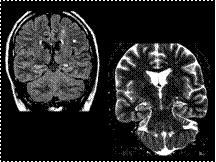
Slide 30
Findings: The left hippocamal formation is smaller than the right side (primarily the body, but also the head and tail somewhat). There is also increased T2 signal intensity of the left hippocampus compared to the right. Incidental note made of changes compatible with small vessel ischemic disease.
Mesial temporal sclerosis (this case is pathognomonic with these findings).
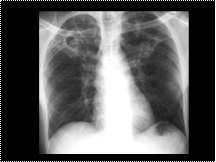
Slide 31
FUNGAL BALL
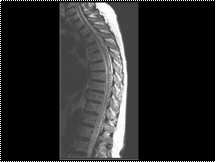
Slide 32
Dural arteriovenous fistula. T2W MRI showing multiple enlarged vessels on the posterior surface of the spinal cord
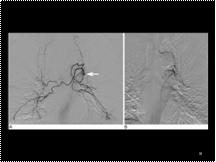
Slide 33
bronchial a.embolisation
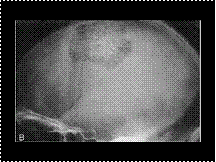
Slide 34
Hemangioma skull
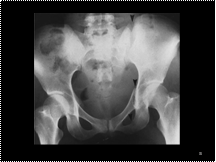
Slide 35
A Malgaigne fracture. Note fractures in the left superior and inferior pubic rami, and in the posterior portion of the left iliac wing adjacent to the sacroiliac joint (arrowheads). There is superior displacement of the left hemipelvis, including the hip.
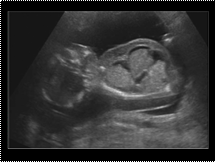
Slide 36
Fetal hydrops. Longitudinal view of a fetus with skin oedema, ascites and a hydrothorax.
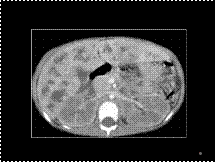
Slide 37
Caroli's ds with central dot sign

Slide 38
DDH
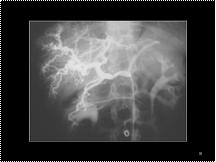
Slide 39
corkscrew app.-Cirrhosis-enlarged hepatic a.with tortous branches
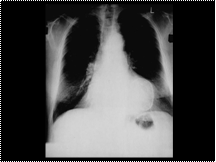
Slide 40
CALCIFIED LEFT VENTRICULAR ANEURYSM
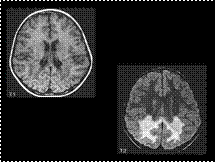
Slide 41
Adrenoleukodystrophy-occipital lobe & spelnium of corpus callosum predeliction
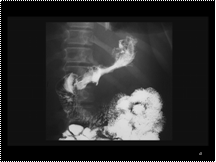
Slide 42
adenoca stomach-small irregular stomach with irregular thick folds
Slide 43
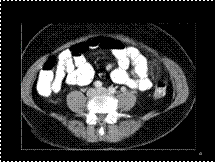
epiploic appendagitis
Slide 44
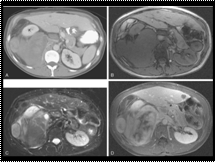
Retroperitoneal mixed well-differentiated and dedifferentiated liposarcoma
Slide 45
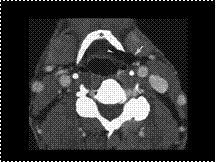
Mixed laryngocele. Enhanced computed tomography reveals an air-filled laryngocele straddling the thyrohyoid membrane. The internal component (arrowhead) is medial to the hyoid bone (asterisk), and the external component (arrow) is lateral to the hyoid.
Slide 46
ADMANTINOMA
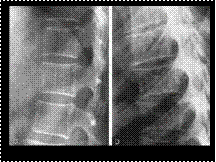
Slide 47
HEMANGIOMA
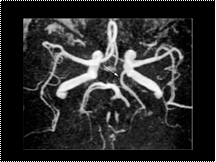
Slide 48
Fetal origin of the posterior cerebral artery. A 3D TOF MRA of the circle of Willis shows a fetal origin of the left posterior cerebral artery (arrow), which arises from the left internal carotid artery and is associated with hypoplasia of the left P1 segment.
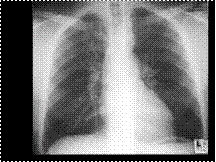
Slide 49
REVERSE 3 SIGN OF COA
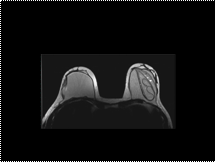
Slide 50
Intracapsular implant rupture. On these T2-weighted fast spin-echo images, the plastic shell of the left breast implant can be seen floating within the silicon, producing a wavy line or linguini sign. Note the presence of a couple of bright dots of water-like material, the salad oil sign
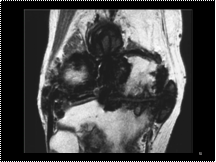
Slide 51
Pigmented villonodular synovitis (PVNS). Coronal T1-weighted MR image showing dark synovial masses due to haemosiderin deposition against a background of degenerative joint disease.