Spotters 4
Slide 2
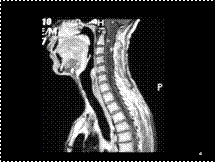
LARGE SEGMENT, INCLUDING END OF BONE
TRIANGULAR OR "FLAME-SHAPED" OR "BLADE OF GRASS" TERMINATION
CORTEX THICK BUT VERY POROUS
PAGET DISEASE
Slide 3
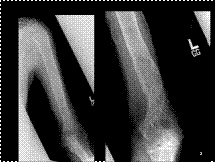
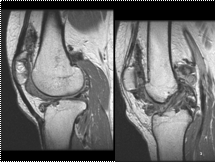
SYNOVITIS
NODULES
DARK SIGNAL (HEMOSIDERIN)
BONE INVASION
PIGMENTED VILLONODULAR SYNOVITIS (PVNS) : A benign proliferative disorder of uncertain etiology that affects synovial joints, bursae, and tendon sheaths. Patients aged 20-50 years. Monoarticular Knee (about 80% of patients)
NODULES
DARK SIGNAL (HEMOSIDERIN)
BONE INVASION
PIGMENTED VILLONODULAR SYNOVITIS (PVNS) : A benign proliferative disorder of uncertain etiology that affects synovial joints, bursae, and tendon sheaths. Patients aged 20-50 years. Monoarticular Knee (about 80% of patients)
Slide 4
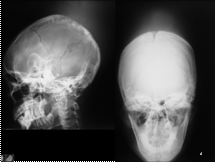
EWINGS SARCOMA
Slide 5
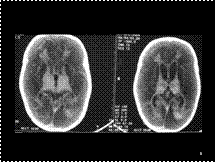
HIE
Slide 6
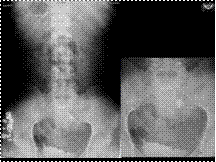
PANCAKE KIDNEY
Slide 7
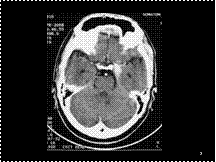
HYPERDENSE BASILAR ARTERY THROMBUS
Slide 8
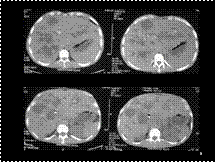
CAROLI DISEASE WTH INTRADUCTAL CALCULI
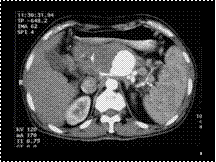
Slide 9
SPLENIC ARTERY PSEUDOANEURYSM
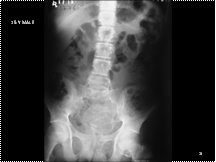
Slide 10
D/D: ABC/GCT before fusion epiphysis
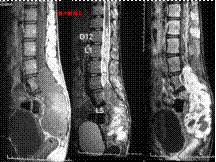
Slide 11
SCHWANNOMA
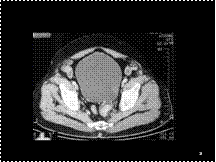
Slide 12
UB DIVERT WITH CALCULUS
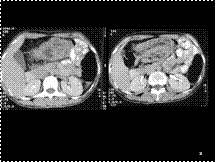
Slide 13
J J INTUSSUCEPTION
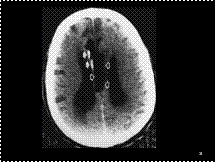
Slide 14
Lipoma of the corpus callosum. Extremely low-density mass (open arrows) involving much of the corpus callosum. Note the peripheral calcifications (closed arrows).
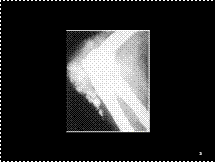
Slide 15
Gout-large calcified tophi in olecranon bursa.
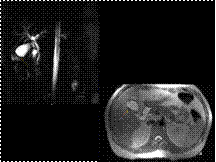
Slide 16
GB ADENOMYOMATOSIS
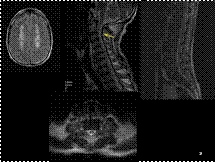
Slide 17
B12 Deficiency- Cord & Brain Involvement
There is associated white matter involvement along with posterior column involvement which is relatively less commonly reported in B12 deficiency. This is 51 year old male who is non alcoholic, with possibly dietary deficiency.
There is associated white matter involvement along with posterior column involvement which is relatively less commonly reported in B12 deficiency. This is 51 year old male who is non alcoholic, with possibly dietary deficiency.
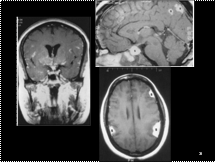
Slide 18
Sarcoidosis. (A) Coronal postcontrast T1-weighted image shows abnormal pial enhancement. There is also abnormal enhancement along the perivascular spaces for the lenticulostriate arteries and in the pituitary stalk. (B) Midsagittal postcontrast T1-weighted image (different patient) shows sarcoid deposits (s) in the posterior interhemispheric fissure and in the sella. (C) Axial postcontrast T1-weighted image of a different patient shows dural and masslike (s) sarcoid deposits simulating meningiomas (avascular at angiography).
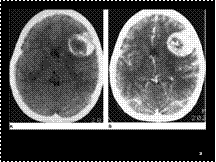
Slide 19
Oligodendroglioma. (A) Nonenhanced scan showing a hypodense mass containing amorphous areas of calcification. (B) After the intravenous injection of contrast material, there is marked contrast enhancement
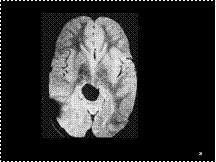
Slide 20
Teratoma. Axial T2-weighted MR image shows a pineal mass that is markedly hypointense because of high fat content and extensive calcification
Slide 21
Cholangiogram & MRCP CDC II
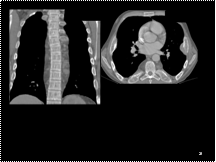
Slide 22
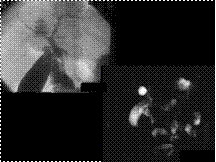
The ribs are widened and display coarse trabeculation consistent with extramedullary hematopoesis (red arrow). Hyperemia of the pulmonary circulation is present
Slide 23
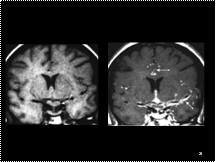
1.Sarcoidosis:Great mimicker leptomeningeal,dural & parenchymal lesions. Isointense on T1W images, hypointense on T2W image
2.Leptomeningeal lesions enhance
2.Leptomeningeal lesions enhance
Slide 24
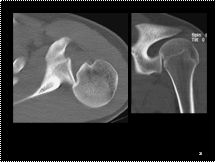
Posterior shoulder dislocation: Axial CT image of the shoulder
shows the humeral head locked behind the posterior glenoid rim,
and adjacent deformity of the anteromedial humeral head indicating
a Reverse Hill-Sachs impaction fracture (Trough sign).
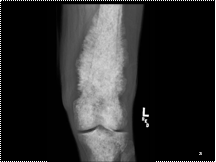
Slide 25
SOFT TISSUE EXTENSION THROUGH
INTACT CORTEX (PERMEATION)
DENSITY ? CORTEX
CLOUD-LIKE AND LINEAR
MINERALIZATION MULTIFOCAL
PROSTATE METASTASES Most skeletal metastases do NOT produce a soft tissue mass
INTACT CORTEX (PERMEATION)
DENSITY ? CORTEX
CLOUD-LIKE AND LINEAR
MINERALIZATION MULTIFOCAL
PROSTATE METASTASES Most skeletal metastases do NOT produce a soft tissue mass

Slide 26
LCH :Thickened stalk ..T2 hyperintense..Intense enhancement
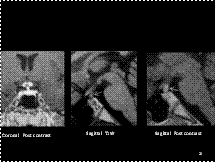
Slide 27
Parotid sialogram showing globular sialectasis.
Collections of contrast medium 1-2 mm in diameter are evenly
distributed throughout the gland (one has been identified with an
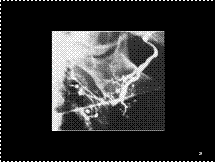
Slide 28
Sub-ungual Exostosis

Slide 29
Facial nerve Schwannomas
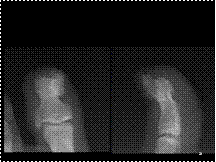
Slide 30
Hemangioma
Retained internal trabeculae
Low attenuation
Mildly expansile
Multifocal
Retained internal trabeculae
Low attenuation
Mildly expansile
Multifocal
Slide 31
Candida oesophagitis. (A) Mucosal plaques. (B) Extensive mucosal nodularity
Slide 32
Gastric volvulus: supine. Gas-filled, grossly dilated stomach, spherical in outline. Note also the linear gas within the wall of the stomach and visualization of both sides of the stomach wall indicating free gas. At laparotomy a perforated gangrenous stomach had undergone volvulus around its transverse axis.
Slide 33
LISSENCEPHALY
Slide 34
RE SYNAPSIS
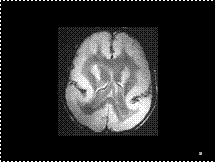
Slide 35
TS
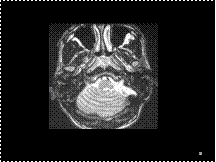
Slide 36
KIENBOCK
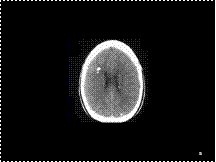
Slide 37
Findings: The left hippocamal formation is smaller than the right side (primarily the body, but also the head and tail somewhat). There is also increased T2 signal intensity of the left hippocampus compared to the right. Incidental note made of changes compatible with small vessel ischemic disease.
Mesial temporal sclerosis (this case is pathognomonic with these findings).
Mesial temporal sclerosis (this case is pathognomonic with these findings).
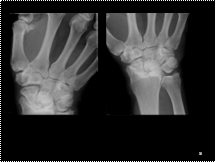
Slide 38
LT ILIAC ARTERY ANEURYSM
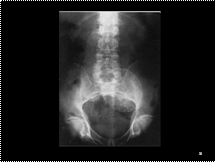
Slide 39
Angiomyolipoma with both well-defined focal and diffuse infiltrating characteristics in a 17-year-old girl with tuberous sclerosis
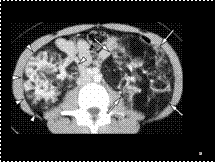
Slide 40
CT image shows randomly arranged cysts in both lungs IN TS
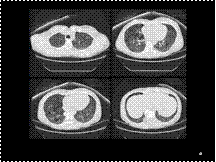
Slide 41
SPINAL HEMANGIOBLASTOMA