Spotters 7
Slide 2
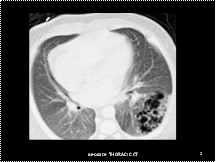
Type II malformation in a neonate with dyspnea. A complex mass with multiple, small, thin-walled cysts (each <1 cm in diameter) is seen in the left lower lobe. There is contralateral mediastinal shift
Slide 3
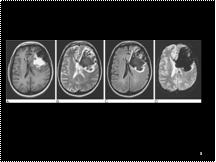
Haematoma. A patient presents with a history suggestive of subarachnoid haemorrhage but MRI shows an extensive left frontal haematoma. The haemoglobin in the haematoma is in different stages of breakdown as shown on (A) the spin-echo T1- and (B) fast spin-echo T2-weighted images. (C) Note the high signal rim on FLAIR imaging indicative of oedema. (D) Gradient-echo sequences are very sensitive for acute haemorrhage and show prominent ‘blooming’ of reduced signal due to susceptibility effects.

Slide 4
MDCT images of a gastroduodenal artery pseudoaneurysm. (A) An axial image demonstrates an enhancing pseudoaneurysm cavity surrounded by a large haematoma in the region of the pancreatic head. (B) A sagittal MPR image demonstrates a pseudoaneurysm arising from the gastroduodenal artery. (C) A further sagittal MPR image demonstrates that the right hepatic artery, from which the gastroduodenal artery arises, originates from the superior mesenteric artery.
Slide 5
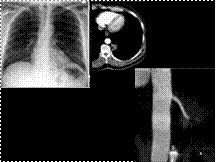
pulmonary sequestration. (A) The CXR demonstrates a mass projected through the left side of the cardiac silhouette. (B) An axial image from an MDCT examination demonstrates a left paraspinal soft-tissue mass. A feeding vessel arising from the thoracic aorta is visible. (C) MPR and (D) VR images show the full length of the oblique course of feeding artery.
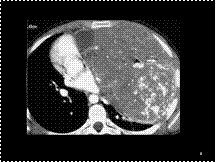
Slide 6
Teratocarcinoma. A large anterior mediastinal, soft tissue mass containing calcifications displaces the mediastinal structures to the right.
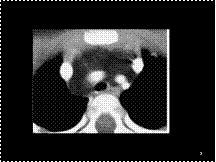
Slide 7
Thymolipoma. A: axial CT scan in a young child shows a fat attenuation mass with minimal soft tissue stranding.
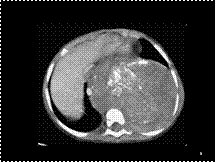
Slide 8
Ganglioneuroma in a 4-year-old girl. A large left paraspinal mass with coarse calcifications extends into the spinal canal and also crosses the midline anterior to the vertebral body.
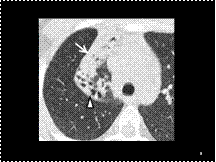
Slide 9
Right upper lobe collapse. The collapsed lobe appears as a triangular structure, marginated laterally by the minor fissure (arrow) and posteriorly by the major fissure (arrowhead). Air is seen in dilated bronchi due to bronchiectasis.
Slide 10
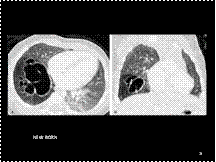
Cystic adenomatoid malformation. Type I lesion; newborn boy with cystic mass seen on in utero sonogram. Axial (A) and coronal (B) reformatted CT scans. An air-filled, thin-walled, multicystic mass with several cysts >1 cm in diameter is present in the right lower lobe. The mediastinum is shifted to the left.
Slide 11
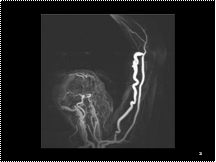
A surgically created dialysis (arteriovenous) fistula in the left arm of patient with chronic renal failure.
Slide 12
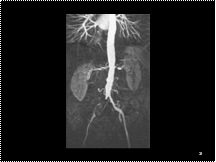
Severe left renal artery stenosis and right common iliac artery occlusion.
Slide 13
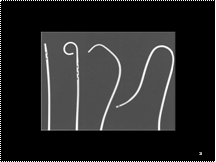
From left to right: straight flush; pigtail; cobra; and sidewinder. Note the side-ports in some of the catheters.
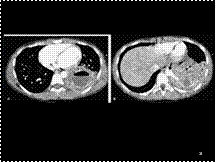
Slide 14
Intralobar pulmonary sequestration. A: Axial CT scan shows a cystic mass with an enhancing rim and air–fluid level, representing an abscess. B: A scan at a lower level shows the anomalous artery (arrow) supplying the pulmonary sequestration.
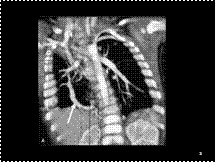
Slide 15
Hypogenetic lung syndrome with partial anomalous venous drainage, neonate. Coronal maximum-intensity projection scan (A) and posterior 3D volume-rendered image (B) show an anomalous vein (arrow) coursing through the right lower lobe to enter the inferior vena cava. Note also the small right hemithorax and the ipsilateral mediastinal shift.
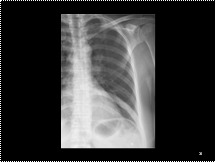
Slide 16
Fibrous dysplasia in a rib; chest radiograph detail of the left lung. Compared with the other ribs the ninth rib shows an increase in density and is slightly broadened.
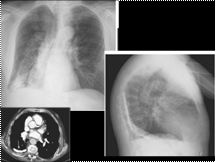
Slide 17
16 Pleural calcification. (A,B) On the chest radiograph an extensive sheet-like calcification of the right pleura with additional pleural thickening (old tuberculous empyema) is seen. (C) CT demonstrates the extent and thickness of the pleural calcification (arrow).
Slide 18
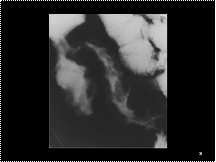
Cobblestoning of the terminal ileum, thickening of the wall of the terminal ileum, and an enlarged ileocaecal valve in Crohn's disease.
Slide 19
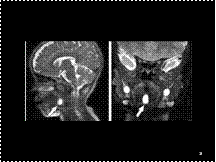
Thyroglossal duct cyst in a 3-year-old boy. Sagittal (a) and coronal (b) T2-weighted
MR images show a hyperintense midline cystic mass of the foramen cecum (arrow).
Slide 20
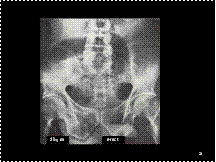
Femoral hernia
Slide 21
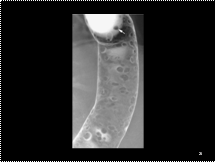
DCBE view of the descending colon in FAP with multiple small polyps about 5 mm in size creating ring shadow menisci around their bases, or as a filling defect in the barium pool (arrow).
Slide 21
DCBE view of the descending colon in FAP with multiple small polyps about 5 mm in size creating ring shadow menisci around their bases, or as a filling defect in the barium pool (arrow).
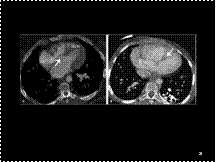
Slide 22
Ventricular septal defect (VSD). A: Perimembranous VSD. CT shows a communication (arrow) between the right and left ventricles at the level of the subaortic septum. Right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH) is also noted in this neonate with tetralogy of Fallot.
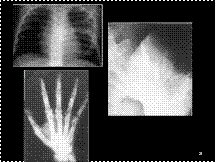
Slide 23
Tuberous sclerosis in an 8-year-old boy
with seizures, developmental delay, and renal hamartomas.
Frontal chest radiograph shows sclerosis and widening
isolated to the left fifth rib.
Tuberous sclerosis. Flame-shaped areas of sclerosis in the iliac blades.
Tuberous sclerosis in the hands. Cyst-like defects are seen in
the bones, both beneath the fingernails and more proximally. Cortical
defects and periostitis are also present
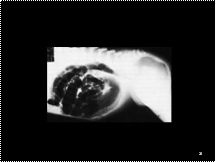
Slide 24
Imperforate anusDue to failure of descent and seperation of hind gut and GU tract during 2nd trimester
Associated with other anomalies: VATER
High, intermediate or low variety
Low intestinal obstruction
Slide 25
admantinoma
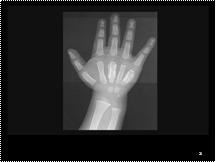
Slide 26
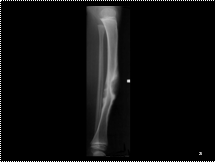
Periosteal reaction, third and fifth metacarpals.
Dactylitis (Hand-Foot syndrome).
sickle cell disease.
Due to infarcts in small tubular bones of hands and feet
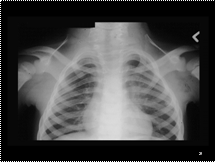
Slide 27
Sprengel’s
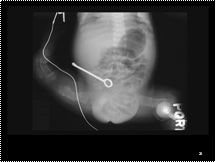
Slide 28
Oi wid hernia
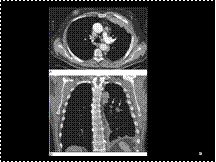
Slide 29
CT cisternography. Thin-section (1.5 mm) slices at the (A) level of the olfactory grooves and (B) foramen ovale. The intrathecal contrast outlines the subarachnoid space and extends into the optic nerve sheaths, outlining the optic nerves. ca = carotid artery, fo = foramen ovale, oc = optic chiasm, ob = olfactory bulb, on = optic nerve, ss = sphenoid sinus, vc = vidian canal
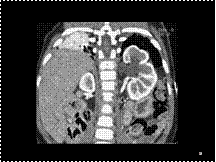
Slide 30
Malignant mesothelioma. (A, B: axial and coronal CT) Diffuse lobulated and nodular thickening of the pleura with tumour extension into the lobar fissure (arrows). Note the metastatic enlargement of some hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes.
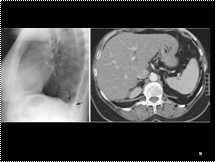
Slide 31
Bochdalek hernia. (A) Lateral chest radiograph shows a focal bulge on the diaphragmatic contour just above the posterior costophrenic recess (arrows). (B) CT shows a fatty mass abutting the defect in the posteromedial aspect of the left hemidiaphragm (arrowheads).
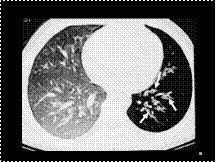
Slide 32
Swyer–James syndrome. Expiratory HRCT scan through the lower lung zones shows a small left lung with bronchiectasis (arrows) and decreased vascularity. The decreased attenuation, compared with the right lung, indicates air trapping.
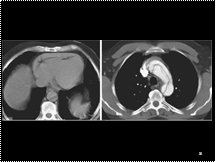
Slide 33
Bochdalek hernia. Coronal CT scan of a neonate shows displacement of the left kidney into the left hemithorax.
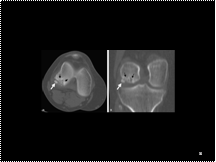
Slide 34
Osteochondritis dissecans. Axial CT scan (A) and coronal reformation (B) show a fragmented, ovoid, low-attenuation, osteochondral defect (black arrows) in the medial femoral condyle. A small fragment of this lesion (white arrow) is displaced into the joint space.

Slide 35
INVASIVE THYMOMA
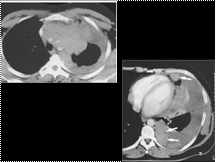
Slide 36
Large haemopericardium complicating a type A aortic dissection. This is an unenhanced image and the haemopericardium is the same density as soft tissue structures (compare to A). (C) The dissection flap can be seen on this enhanced CT within the transverse arch.
Slide 37
lipoMMC
Slide 38
cdc

Slide 29
CT cisternography. Thin-section (1.5 mm) slices at the (A) level of the olfactory grooves and (B) foramen ovale. The intrathecal contrast outlines the subarachnoid space and extends into the optic nerve sheaths, outlining the optic nerves. ca = carotid artery, fo = foramen ovale, oc = optic chiasm, ob = olfactory bulb, on = optic nerve, ss = sphenoid sinus, vc = vidian canal

Slide 30
Malignant mesothelioma. (A, B: axial and coronal CT) Diffuse lobulated and nodular thickening of the pleura with tumour extension into the lobar fissure (arrows). Note the metastatic enlargement of some hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes.

Slide 31
Bochdalek hernia. (A) Lateral chest radiograph shows a focal bulge on the diaphragmatic contour just above the posterior costophrenic recess (arrows). (B) CT shows a fatty mass abutting the defect in the posteromedial aspect of the left hemidiaphragm (arrowheads).

Slide 32
Swyer–James syndrome. Expiratory HRCT scan through the lower lung zones shows a small left lung with bronchiectasis (arrows) and decreased vascularity. The decreased attenuation, compared with the right lung, indicates air trapping.

Slide 33
Bochdalek hernia. Coronal CT scan of a neonate shows displacement of the left kidney into the left hemithorax.

Slide 34
Osteochondritis dissecans. Axial CT scan (A) and coronal reformation (B) show a fragmented, ovoid, low-attenuation, osteochondral defect (black arrows) in the medial femoral condyle. A small fragment of this lesion (white arrow) is displaced into the joint space.

Slide 35
INVASIVE THYMOMA

Slide 36
Large haemopericardium complicating a type A aortic dissection. This is an unenhanced image and the haemopericardium is the same density as soft tissue structures (compare to A). (C) The dissection flap can be seen on this enhanced CT within the transverse arch.

Slide 37
lipoMMC

Slide 38
cdc